
Relative position
This position place the element relative to its normal flow position. Relative position elements are still in the normal document flow. Using Left, Right, Top and Bottom properties, relative position elements can be shifted from its normal flow position.
What is Normal flow?
Rendering elements normally one after another is considered normal flow. Each normal flow element position affects or affected by other normal flow elements.
Example:
.box2 {
position:relative;
top:100px;
left:40px;
}
Note: Without position properties (top, left, right, bottom), Static and Relative position results are same.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Relative Position</title>
<style>
div {
width: 300px;
height:100px;
border:1px solid;
font-size:20px;
}
#div2 {
position:relative;
top:40px;
left:270px;
}
#div3 {
position:relative;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>Element with default position(static).</div>
<div id="div2">Element with Relative position. top:40px; left:270px;</div>
<div id="div3">Element with Relative position. top:0px; left:0px;
(default value assigned since there is no position value specified.)</div>
</body>
</html>
Result:

Image1:
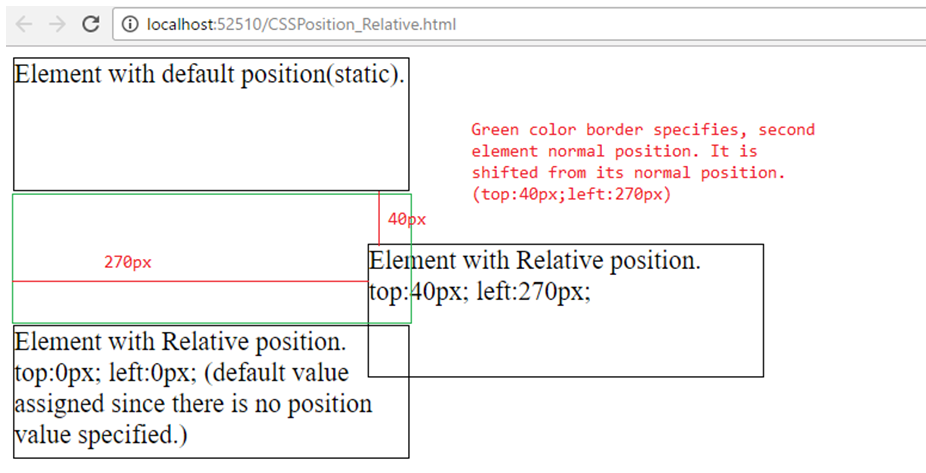
In the above example,
- Three DIV elements are there.
- First element position is default position (static).
-
Second element position is relative. As per left and top properties, this element is shifted (top:40px; left:270px;) from its normal positon.
Note: Using green color border, second element normal position is marked (image1).
-
Third element position is relative. But no position properties (top, left, right, bottom) are specified. So default position property
value (0) is assigned to top and left properties. This is placed / positioned next to second element normal position.
Note: Using green color border, second element normal position is marked (image1).