
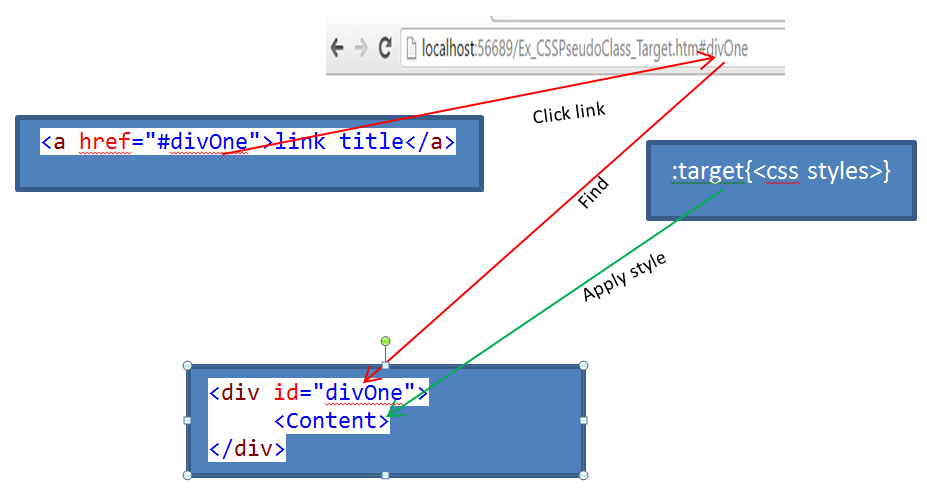
Pseudo-Class - :target
Selects an element which is specified in the referring URI (# followed by element id).
Example 1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS pseudo-class selector - :target</title>
<style>
:target {
font-size: large;
border:2px solid red;
display:block;
}
div {
display:none;
}
body {
width:500px;
border:1px solid green;
padding:20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<a href="#divOne">1) Restaurant section</a> <br />
<a href="#divTwo">2) Electronics section</a>
</p>
<div id="divOne">
<p><b>Restaurant section:- </b></p>
<p>Restaurant section has many restaurants and serves different types of foods.</p>
</div>
<div id="divTwo">
<p><b>Electronics section:-</b> </p>
<p>Electronics section has various types of electronic items.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Result:
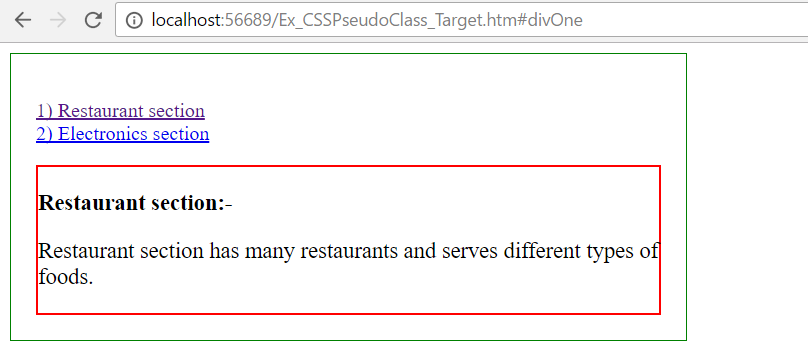
In the above example,
- When user clicks first link (“Restaurant section”) then restaurant section is displayed.
- When user clicks second link (“Electronics section”) then electronics section is displayed.
Example 2: Set different target pseudo class to different element groups.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS pseudo-class selector - :target</title>
<style>
div:target {
font-size: large;
border:2px solid red;
display:block;
}
p:target {
border:5px solid gray;
}
body {
width:500px;
border:1px solid green;
padding:20px;
}
.headSection {
font-weight:bold;
padding:5px;
background-color:green;
color:white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<a href="#divOne">1) Restaurant section</a> <br />
<a href="#divTwo">2) Electronics section</a> <br />
<a href="#pThree">3) *** Note *** </a>
</p>
<div id="divOne">
<p class="headSection"> Restaurant section:- </p>
<p>Restaurant section has many restaurants and serves different types of foods.</p>
</div>
<div id="divTwo">
<p class="headSection"> Electronics section:- </p>
<p>Electorinics section has various types of electronic items.</p>
</div>
<p id="pThree">
<span class="headSection">Note:-</span>
1) Enough parking is available.
2) Public transport is well connected to this mall location.
</p>
</body>
</html>
Result:
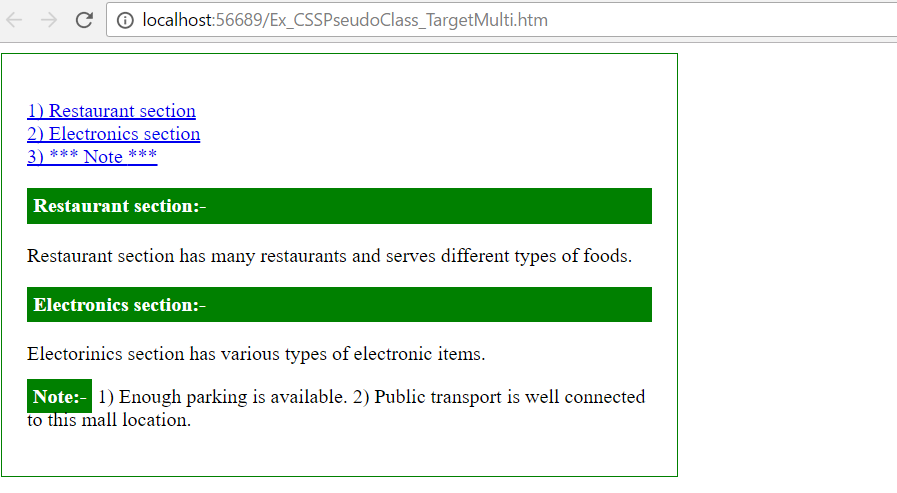
1) When page loads (without any link click)
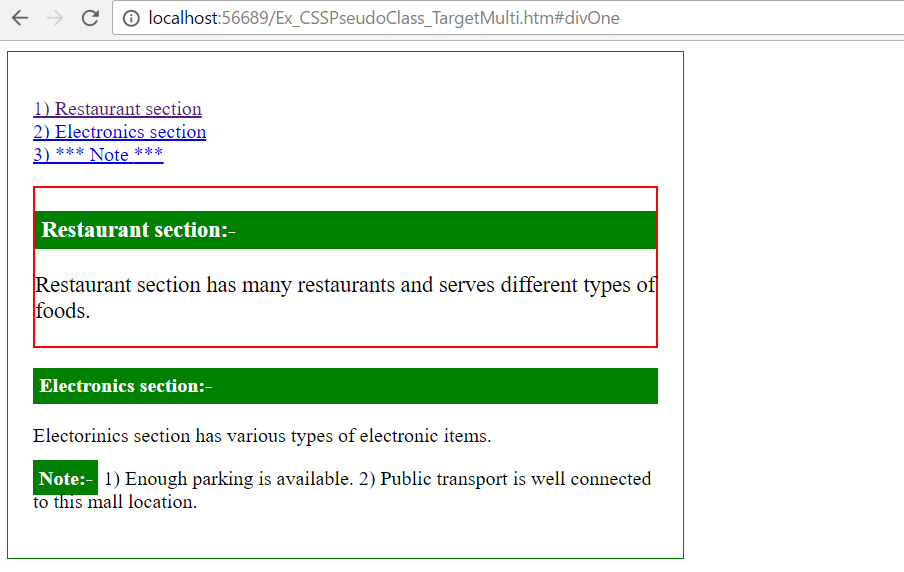
2) When click “Restaurant section” link
3) When click “Note” link
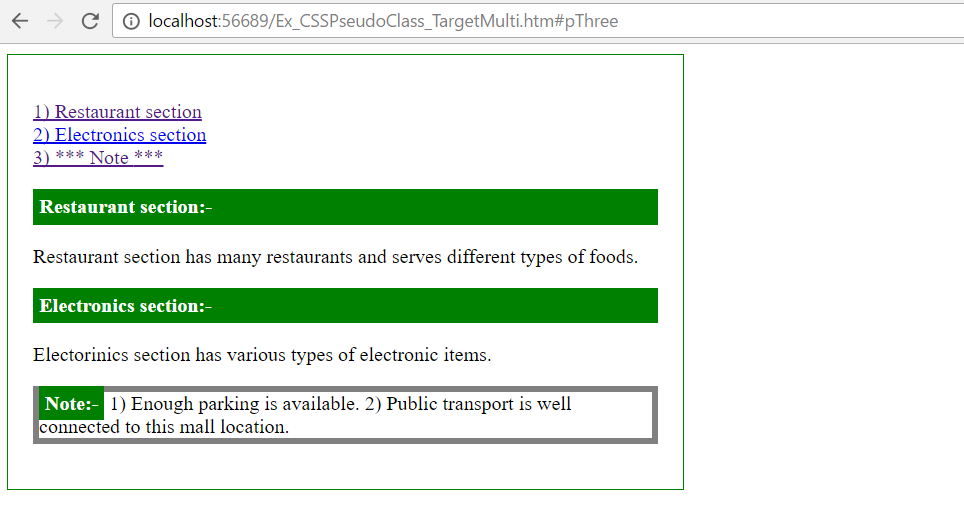
In the above example,
- Anchors (href="#divOne", href="#divTwo") are linked with two different DIV elements ("#divOne" , "#divTwo").
- Anchor (href="#pThree") is linked with P element ("#pThree").
- Based on Anchor (href) click, related pseudo target class (div:target{} OR p:target{}) styles are applied.