
CSS Position
Web applications are always growing, and users expect so much information on a single page with less click or scroll. Placing/Positioning HTML elements at correct places are the key to hold so many controls on a single page. CSS position is one of the key topics in CSS which helps to understand how to place HTML elements at various locations on a page.
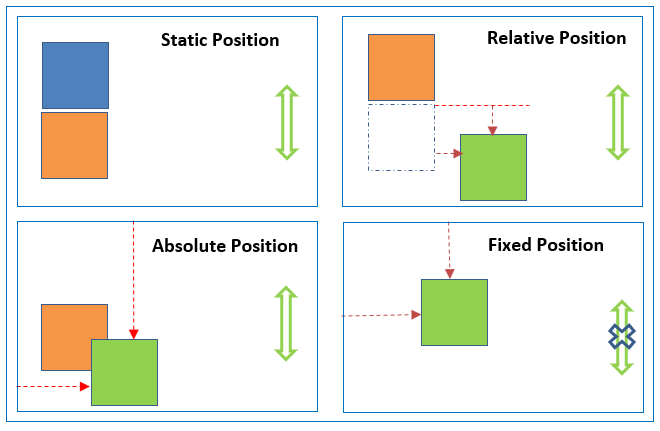
What is document normal flow?
Rendering elements normally one after another is considered as normal flow. Each normal flow element position affects or affected by other normal flow elements.
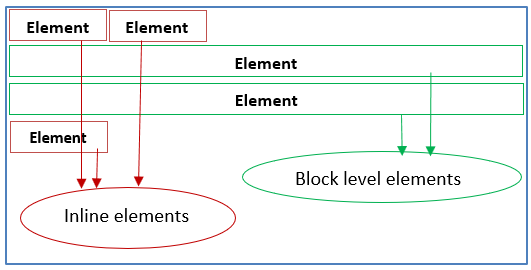
HTML Element categories.
Two types of HTML elements categories are there. One is Block level elements(ex: <div></div>,<p></p>) and another one is Inline elements(<span></span>, <img />). Every block level element starts a new line and occupies full width and Inline elements only occupy required space. Position properties can be applied to both category elements.
There are five types of CSS position properties are there.
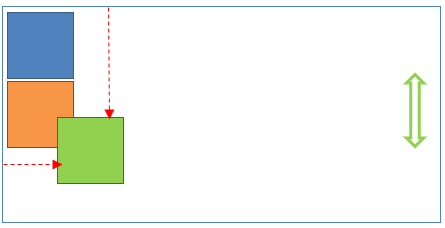
1 Static position
This is the default CSS position applicable to all HTML elements. This position place the HTML elements based on normal document flow. Using this position, top/right/bottom/left properties can not be applicable to elements (ie., static position elements don’t obey top/right/bottom/left properties).
Note: Page scrolling does affect this position.

.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:cornflowerblue;
position:static;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
}<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
</body>2 Relative position
This position places the element relative to its normal position. This position is relative to normal document flow. Here top/right/bottom/left properties can be applied to elements.
Note:
- Page scrolling does affect this position.
- If position only applied without top/right/bottom/left properties, it will act like Static position.
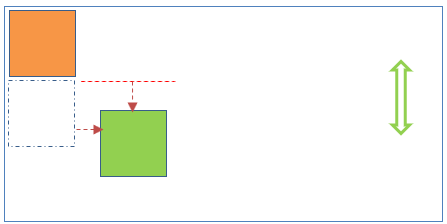
.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:relative;
left:60px;
top:20px;
}<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
</body>3 Absolute position
This position places the element at the exact position specified.
This position is relative to
- its parent element position when parent element position is relative/absolute.
- document body (browser viewport) when parent element position is static.
- document body (browser viewport) when there is no parent element.
Note:
- Page scrolling does affect this position.
- This position element is completely removed from normal document flow.
.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:cornflowerblue;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
}
.p3 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:absolute;
left:60px;
top:20px;
}<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
<div class="p3">
</div>
</body>4 Fixed position
This position places the element at a fixed place relative to the viewport. Page scrolling does not affect this position.
Note: This position element is completely removed from normal document flow.

.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:fixed;
left:40px;
top:40px;
}<body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
</body> 5 Sticky position
Sticky position is a combination of relative and fixed. It is relative until it crosses a specified threshold, at which point it is treated as static position.
Many browsers don’t support Sticky position partially/fully. Following image (from https://caniuse.com/#feat=css-sticky) shows Sticky position supporting browsers and its versions.
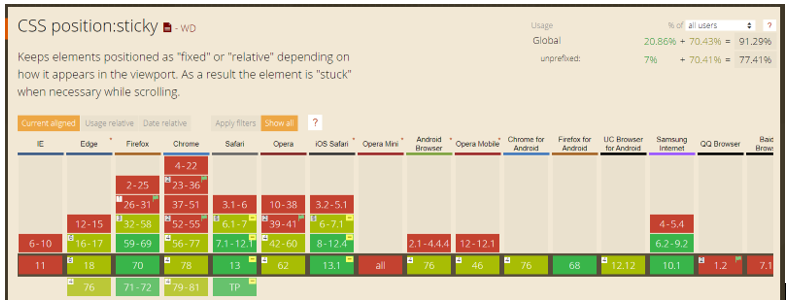
Note: This position element is completely removed from normal document flow.
6 Difference between Relative position and Absolute CSS position (Relative vs Absolute position)
- Relative position places the element relative to its normal position and Absolute position places the element at the exact position specified.
- Relative position elements are placed based on normal document flow, but Absolute position elements are completely removed from normal document flow and place at the exact position.
- Absolute position elements are placed based on either parent element position when parent element position is relative/absolute OR document body (browser viewport).
.p1 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:sandybrown;
position:relative;
left:50px;
top:50px;
}
.p2 {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:absolute;
right:50px;
top:50px;
} <body>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<br/>
<div class="p1">
</div>
<br />
<div class="p1">
</div>
<div class="p2">
</div>
<br />
<div class="p2">
</div>
<br />
<div class="p2">
</div>
</body>
Above example code output is given below.
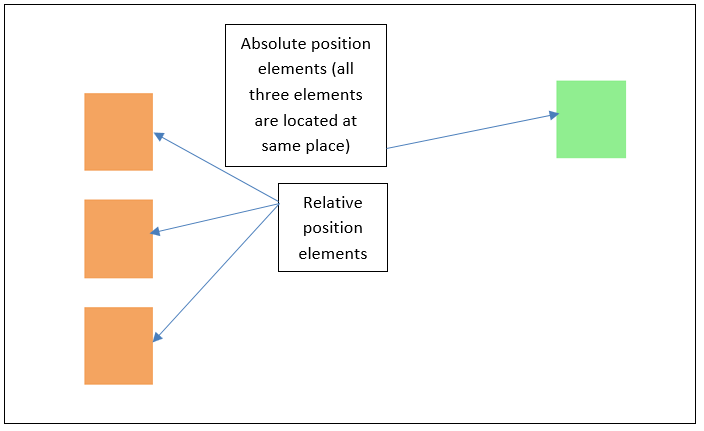
7 Difference between Static position and Relative CSS position (Static position vs Relative position)
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable to static position elements but applicable to Relative position elements.
- Static position is a default position.
8 Static and Relative position similarities
- Relative position works like Static when left/right/top/bottom properties are not applied.
- Relative and Static position elements are placed based on normal document flow.
9 Difference between Static and Absolute CSS position (Static vs Absolute position)
- Static position is a default position.
- Static position elements are placed based on normal document flow, but Absolute position elements are completely removed from normal document flow and place at exact position.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable to Static position elements but applicable to Absolute position elements.
10 Difference between Fixed and Absolute CSS position (Fixed vs Absolute position)
- Absolute position places the element at the exact position specified. This position element scrolls with the HTML page.
- Fixed position works like Absolute position, but it is relative to view port. This position element doesn’t scroll with the HTML page.
Following different situations explains how CSS position works with parent and child elements when parent and child CSS positions are different.
Note: Irrespective of parent element position, if child element position is Static, Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable to child element.
11Static positioning inside default positioning
- Parent element position: No parent element. [In this case document body (browser viewport) is considered as parent element.]
- Child element position: static
Result:
- Child element is placed based on normal document flow.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable child elements.
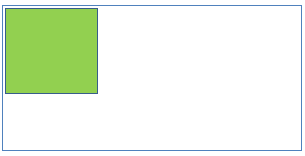
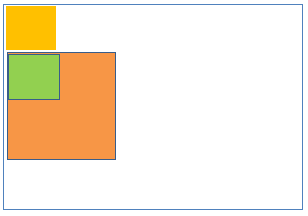
12Static positioning inside Static positioning
- Parent element position:Static
- Child element position:Static
Result:
- Child element position is relative to the parent element position.
- Parent and child elements starting position(x,y) is same.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable to parent and child elements.
- Both elements positions scroll with the HTML page.
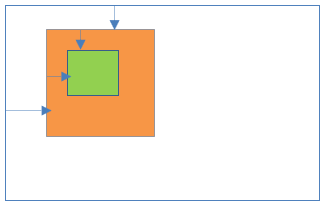
13Relative positioning inside Static positioning
- Parent element position:Static
- Child element position:Relative
Result:
- Child element is relative to its normal position which is inside the parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable to parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to child element and those works relative to its normal position which is inside the parent element.
- Both elements positions scroll with the HTML page.
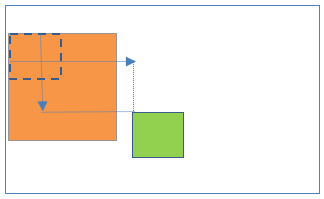
.parent {
width:150px;
height:150px;
background-color:sandybrown;
position:static;
}
.child {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:relative;
left:160px;
top:50px;
}<body>
<div class="parent">
</div>
<br/>
<div class="parent">
<div class="child">
</div>
</div>
</body> 14Absolute positioning inside Static positioning
- Parent element position:Static
- Child element position: Absolute
Result:
- Child element is not relative to parent element. Child element works based on document body (browser viewport).
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
- Both elements positions scroll with the HTML page.
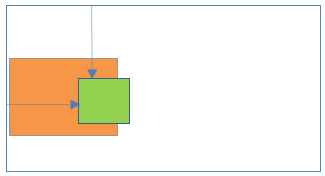
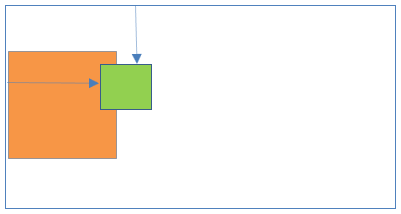
15Fixed positioning inside Static positioning
- Parent element position:Static
- Child element position: Fixed
Result:
- Child element is not relative to parent element.
- This position places the element at fixed place relative to the viewport(not Static parent element).
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
- Child element position is not scroll with the HTML page.
- Parent element position is scroll with the HTML page.
16Relative positioning inside default positioning
- Parent element position:No parent [Note: In this case document body (browser viewport) is considered as parent element.]
- Child element position:Relative
Result:
- Child element position is relative to normal flow.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to child element.
- Child element position is scroll with the HTML page.
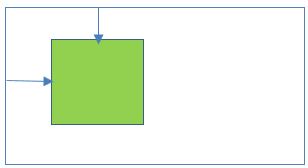
17Static positioning inside Relative positioning
- Parent element position:Relative
- Child element position: Static
Result:
- Child elements is relative to the parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent element only not child element.
- Both elements positions are scroll with the HTML page.
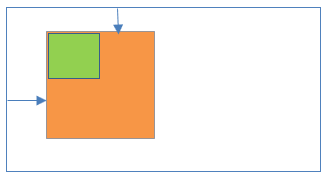
.parent {
width:150px;
height:150px;
background-color:sandybrown;
position:relative;
left:50px;
top:60px;
}
.child {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:static;
} <body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="child">
</div>
</div>
</body>18Relative positioning inside Relative positioning
- Parent element position:Relative
- Child element position:Relative
Result:
- Child element is relative to its parent elements.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent and child element.
- Both elements positions are scroll with the HTML page.
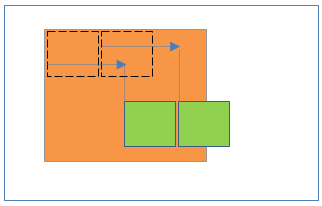
19Absolute positioning inside Relative positioning
- Parent element position:Relative
- Child element position:Absolute
Result:
- Here child element is absolutely placed relative to the parent element position.
- Child element Left/right/top/bottom properties works relative to the parent element position only.
- Both elements positions are scroll with the HTML page.
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
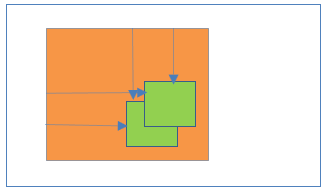
20Fixed positioning inside Relative positioning
- Parent element position:Relative
- Child element position:Fixed
Result:
- Child element is placed at fixed place relative to the viewport not relative to the parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to the parent and child elements.
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
- Child element is not scroll with the HTML page.
- Parent element is scroll with the HTML page.
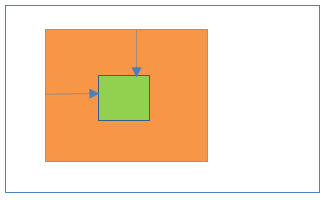
21Absolute positioning inside default positioning
- Parent element position: No parent [Note: In this case document body (browser viewport) is considered as parent element.]
- Child element position:Absolute
Result:
- Here child element is absolutely placed relative to the viewport.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to child element.
- Child element position is scroll with the HTML page.
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
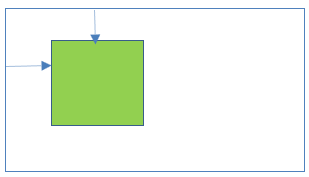
22Static positioning inside Absolute positioning
- Parent element position: Absolute
- Child element position: Static
Result:
- Child element is placed relative to the parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are not applicable to child element.
- Parent and child elements positions are scroll with the HTML page.
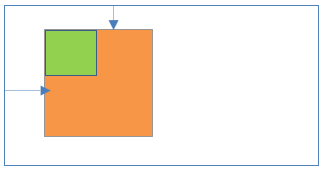
23Absolute positioning inside Relative positioning
- Parent element position:Absolute
- Child element position:Relative
Result:
- Child element is placed relative to its normal position based on parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent and child elements.
- Parent and child elements positions are scroll with the HTML page.
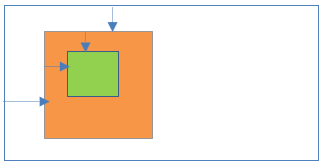
.parent {
width:150px;
height:150px;
background-color:sandybrown;
position:absolute;
left:160px;
top:50px;
}
.child {
width:50px;
height:50px;
background-color:lightgreen;
position:relative;
left:25px;
top:30px;
}
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="child">
</div>
</div>
</body>24Absolute positioning inside Relative positioning
- Parent element position:Absolute
- Child element position:Absolute
Result:
- Child element is absolutely placed and relative to the parent element(Child element positioned based on parent element position).
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent and child elements.
- Parent and child elements positions are scroll with the HTML page.
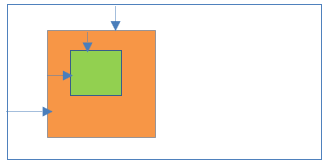
25Fixed positioning inside Absolute positioning
- Parent element position:Absolute
- Child element position:Fixed
Result:
- Child element is placed at fixed place relative to the viewport not relative to the parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to the parent and child elements.
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
- Child element is not scroll with the HTML page.
- Parent element is scroll with the HTML page.
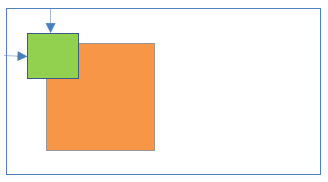
26Fixed positioning inside default positioning
- Parent element position:No parent [Note: In this case document body (browser viewport) is considered as parent element.]
- Child element position:Fixed
Result:
- Child element is placed at fixed place relative to the viewport.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to child element.
- Child element is completely removed from the normal document flow.
- Child element is not scroll with the HTML page.

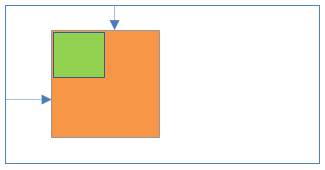
27Static positioning inside Fixed positioning
- Parent element position:Fixed
- Child element position:Static
Result:
- Child element is relative to the parent element and placed on normal flow (1st child element and parent element X & Y positions are same).
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent element only.
- Parent and child elements are not scroll with the HTML page.
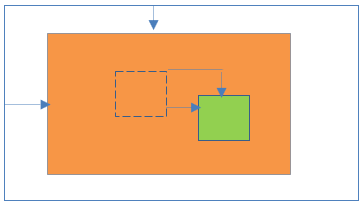
28Relative positioning inside Fixed positioning
- Parent element position:Fixed
- Child element position:Relative
Result:
- Child element is relative to the parent element.
- Child element is placed relative to its normal position based on parent element.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent and child elements.
- Parent element is not scroll with the HTML page. Because of the parent element, child element is also not scroll with the HTML page.
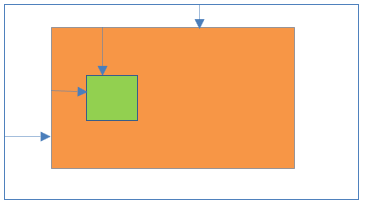
29Absolute positioning inside Fixed positioning
- Parent element position:Fixed
- Child element position:Absolute
Result:
- Child element is absolutely placed and relative to the parent element position.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to child and child elements.
- Parent element is not scroll with the HTML page. Because of the parent element child element is also not scroll with the HTML page.
30Fixed positioning inside Fixed positioning
- Parent element position:Fixed
- Child element position:Fixed
Result:
- Child element is placed at fixed place relative to the parent element not relative to the viewport.
- Left/right/top/bottom properties are applicable to parent and child elements.
- Parent and child elements are not scroll with the HTML page.
Following are the related CSS position properties.
Top, right, bottom, left, float, height, width, overflow, clear, z-index and clearfix technique.
Related topics are explained using the following links.